Giant Pandas
Conservation Status
Vulnerable
Why are Pandas in Danger?
Currently, habitat loss and climate change are some of the largest threats to the Giant Panda. Studies have estimated that nearly half of the remaining habitat will be lost by 2070; however, a recent study found this may have been overestimated and it’s closer to a quarter. Nevertheless, both studies concluded climate change posed a major threat to what little habitat is left.
Other threats to the Giant Pandas including hunting, food shortages, agriculture, urban development, and an unusually long reproductive cycle.
How can we Help?
As home to the only wild populations of Giant Pandas, China has taken substantial lengths to aid in their conservation. Various large programs are emerging in the Sichuan Province of China (which houses nearly 75% of the remaining wild populations) that are aimed at conserving the area and making viable new land more suitable for possible panda reintroduction and translocation.
There is so much we still need to understand about the Giant Panda; however, to ensure we have a healthy restoration population to pull from. Here at PDXWildlife, we work in conjunction with several of the Sichuan Panda conservation programs, including the China Conservation and Research Center for Giant Pandas (CCRCGP) at the Bifengxia Panda Reserve in Ya’an, China, to research some of the most crucial restoration apsects:
a) How to best allow the pandas to select viable mates
b) Determine what factors contribute to the notoriously low reproductive success of captive breeding
c) How to ensure reintroduction populations are best suited for life in the wild

Our Current Projects

Stereotype Behavior
Projects in Process Info Coming Soon…

Male-Male Competition
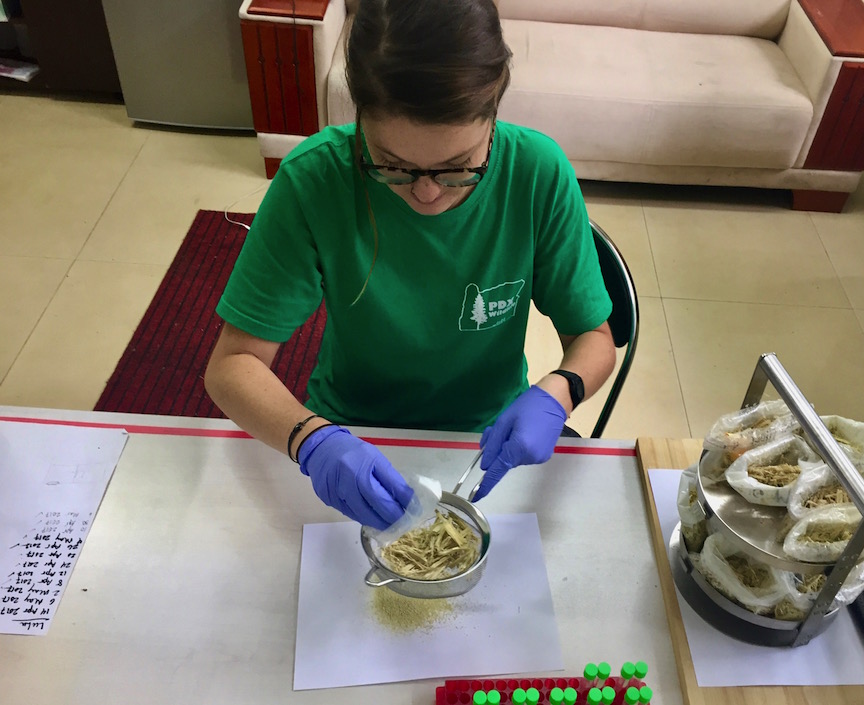

Fecal Hormone Analysis

Personality/ Domestication Effects
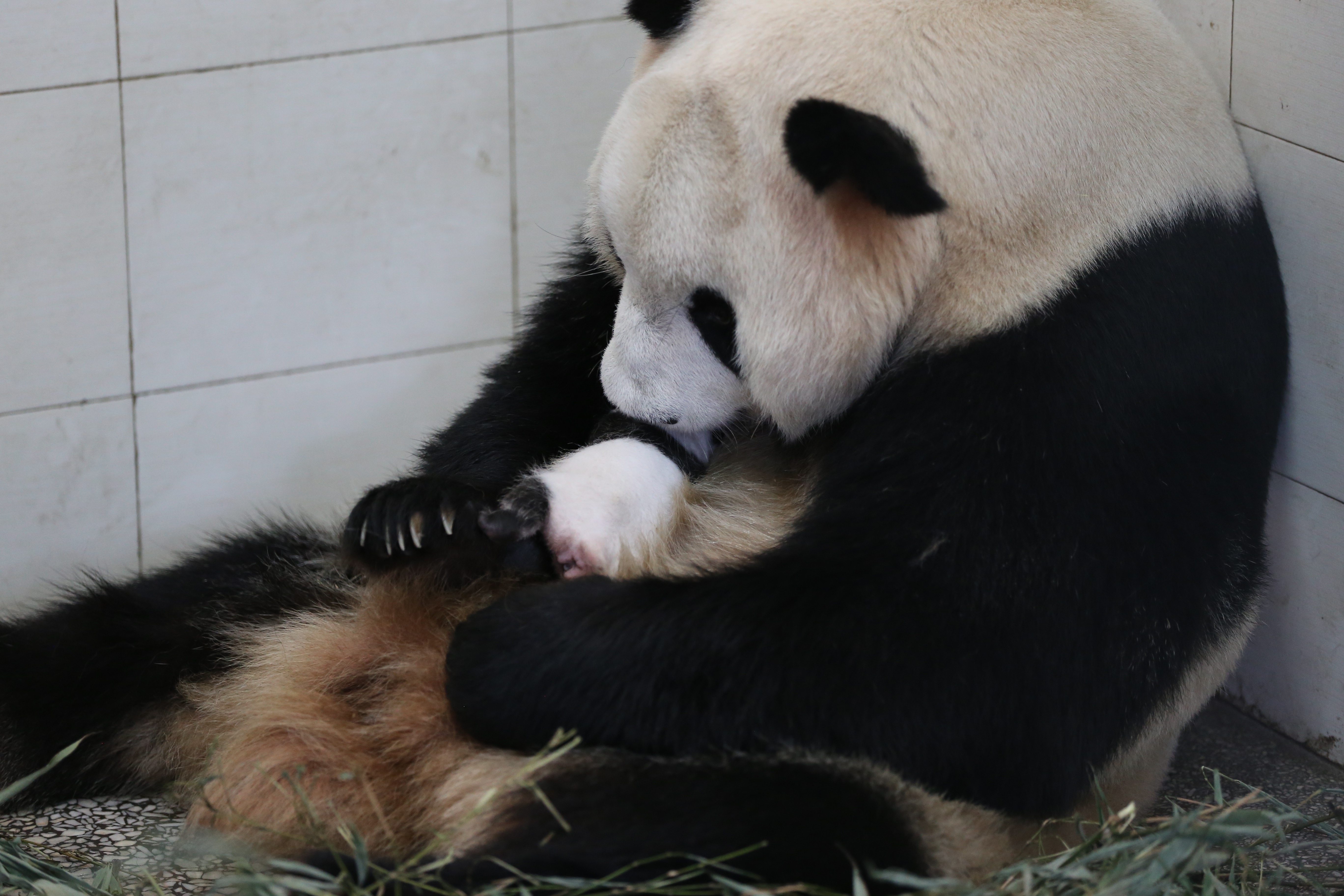

Maternal Care

Blood Lead Levels

Mercury Methylmercury Levels in Captive Pandas